Gum infections are most commonly caused by poor dental care, which allows bacteria to become stuck between the gums and teeth, where it can thrive. A gum infection is caused by bacteria accumulating in the tissue surrounding the teeth.
Bacteria of several sorts abound in the mouth. Brushing and flossing the teeth on a daily basis helps regulate bacteria levels, keeping the mouth, teeth, and gums healthy and preventing tooth decay.
Symptoms
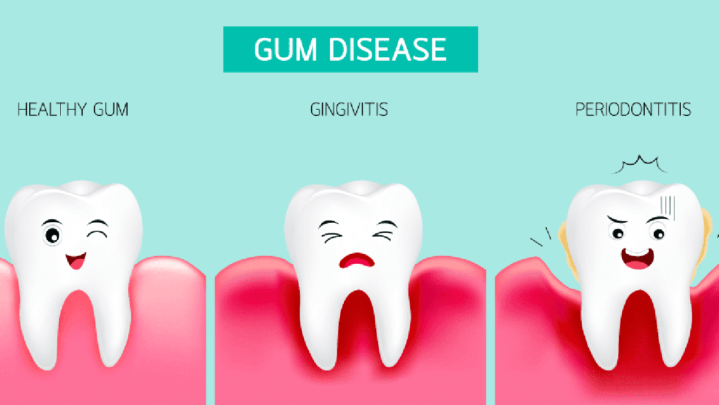
The signs and symptoms of a gum infection vary based on how far the infection has progressed and where it has spread. Gingivitis, a medical name for gum inflammation, is one of the most common symptoms. Gingivitis is characterized by red, swollen gums that bleed easily when the person brushes his or her teeth.
Spitting blood after brushing the teeth, loose teeth, receding gums, changes in how a person chews or how their teeth fit together when they chew, sensitive teeth, pain when chewing, persistent foul breath, pus discharge in the mouth, and so on are all indicators of gum infection or gum disease.
Treatment
To avoid problems, it is critical to treat a gum infection as soon as possible.
1. Cleaning teeth
There are numerous methods for deep cleaning your teeth that do not require surgery. To avoid gum discomfort, they all eliminate plaque and tartar:
Tartar is removed from above and below the gum line during scaling.
Root planing smooths rough regions on the root surface and eliminates plaque and tartar.
Another therapeutic option for improving gum health is laser therapy. A soft-tissue laser is used to treat the gum pocket, which helps to destroy harmful germs deep within the periodontal pockets, remove unhealthy tissue, and stimulate healing.
2. Medications
To disinfect the mouth, use an antiseptic mouthwash containing chlorhexidine.
Antiseptic mouthwash
After root planing, timed-release antiseptic chips containing chlorhexidine can be put into pockets.
Antibiotics
After scaling and planing, antibiotic microspheres produced with minocycline can be placed into pockets.
Antibiotics can be used to treat gum inflammation that persists. Antibiotic doxycycline can help prevent tooth decay caused by enzymes.
Flap surgery
The gums are pulled back as plaque and tartar are removed from deeper pockets during flap surgery. After that, the gums are sutured in place so that they fit securely around the tooth.
Also Read: 5 Benefits Of Daily Early Morning Meditation