Celiac disease, also understood as celiac sprue or gluten-sensitive enteropathy is an immunological response to the protein gluten, which is found in wheat, barley, and rye. Eating gluten causes an immunological reaction in the small intestine if you have celiac disease. This reaction, over time, destroys the lining of your small intestine and stops it from absorbing some nutrients (malabsorption). Diarrhea, lethargy, weight loss, bloating, and anemia are common symptoms of intestinal injury, which can progress to significant consequences. Malabsorption can impact growth and development in youngsters as well as cause the symptoms noticed in adults. Although there is no cure for celiac disease, maintaining a gluten-free diet can help manage symptoms and promote intestinal repair in most people.
Causes
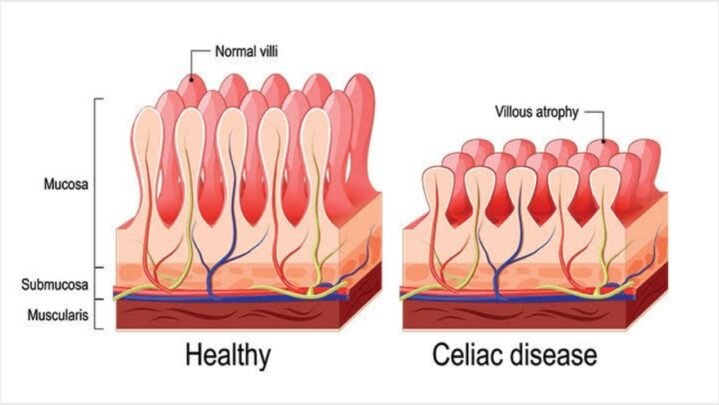
Celiac disease can be caused by your genes, gluten-containing foods, and other factors, but the exact reason is unknown. Infant-feeding patterns, gastrointestinal illnesses, and gut flora may all play a role. Celiac disease can become active following surgery, pregnancy, childbirth, viral infection, or extreme mental stress. When the body’s immune system overreacts to gluten in meals, the reaction damages the small intestine’s tiny, hairlike projections (villi). Villi digest food and absorb vitamins, minerals, and other nutrients. If your villi are damaged, no matter how much you consume, you will not acquire adequate nutrition.
Complications:
Celiac disease, if left untreated, can lead to:
Malnutrition. This happens when your small intestine is unable to absorb adequate nutrition. Anemia and weight loss can result from malnutrition. Malnutrition can induce poor growth and short stature in children.
Bone deterioration. Calcium and vitamin D malabsorption can cause bone softening in children and bone density loss (osteopenia or osteoporosis) in adults.
Miscarriage and infertility. Calcium and vitamin D malabsorption can contribute to reproductive problems.
Lactose sensitivity. After eating or drinking lactose-containing dairy products, you may have abdominal pain and diarrhea due to small intestine damage. You may be able to accept dairy products again once your intestine has recovered.
Credits: Mayo Clinic
Also Read: Healthy Nutrients To Help You Age Slowly